What Causes Accelerated Aging? Research on Senescent Cells - Natural Eye Care Blog: News & Research on Vision

Combined use of dasatinib and quercetin alleviates overtraining-induced deficits in learning and memory through eliminating senescent cells and reducing apoptotic cells in rat hippocampus - ScienceDirect

Senolytic effects of quercetin in an in vitro model of pre-adipocytes and adipocytes induced senescence | Scientific Reports

Prospective Selective Mechanism of Emerging Senolytic Agents Derived from Flavonoids | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry

Senolytic drugs: from discovery to translation - Kirkland - 2020 - Journal of Internal Medicine - Wiley Online Library

Targeting Senescent Cells for a Healthier Aging: Challenges and Opportunities - Song - 2020 - Advanced Science - Wiley Online Library
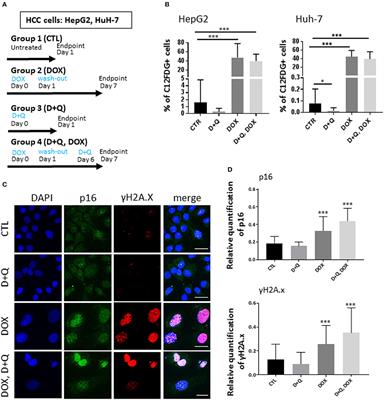
Frontiers | Senolytic Cocktail Dasatinib+Quercetin (D+Q) Does Not Enhance the Efficacy of Senescence-Inducing Chemotherapy in Liver Cancer

Quercetin and RAW 264.7 cell senescence measured using β-galactosidase... | Download Scientific Diagram

Senolytic Cocktail Dasatinib+Quercetin (D+Q) Does Not Enhance the Efficacy of Senescence-Inducing Chemotherapy in Liver Cancer | Semantic Scholar

Dasatinib and quercetin target senescent cells. (A) D is more effective... | Download Scientific Diagram

Senolytics: A Translational Bridge Between Cellular Senescence and Organismal Aging. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Senolytics decrease senescent cells in humans: Preliminary report from a clinical trial of Dasatinib plus Quercetin in individuals with diabetic kidney disease - eBioMedicine

Long-term treatment with senolytic drugs Dasatinib and Quercetin ameliorates age-dependent intervertebral disc degeneration in mice | Nature Communications

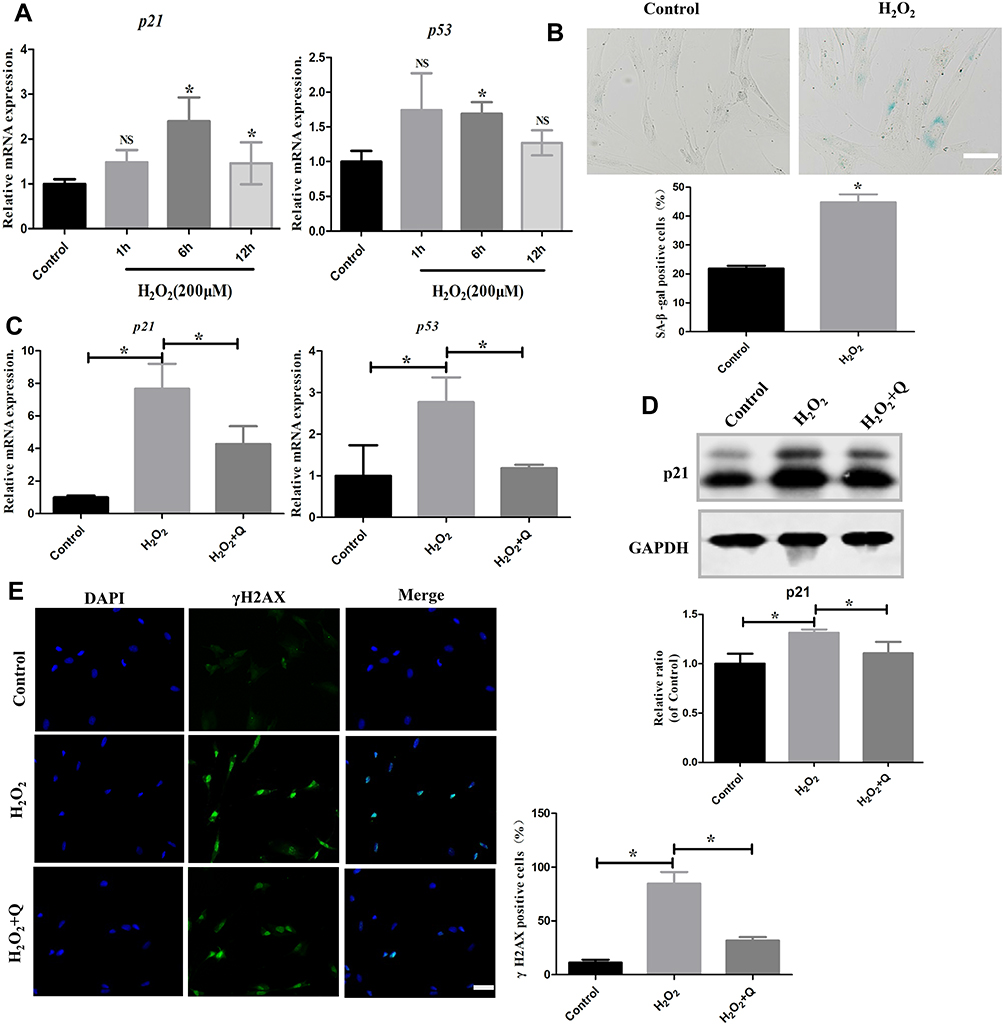
Quercetin ameliorates oxidative stress-induced senescence in rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Study

Senescent skeletal cells cross-talk with synovial cells plays a key role in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis | Arthritis Research & Therapy | Full Text
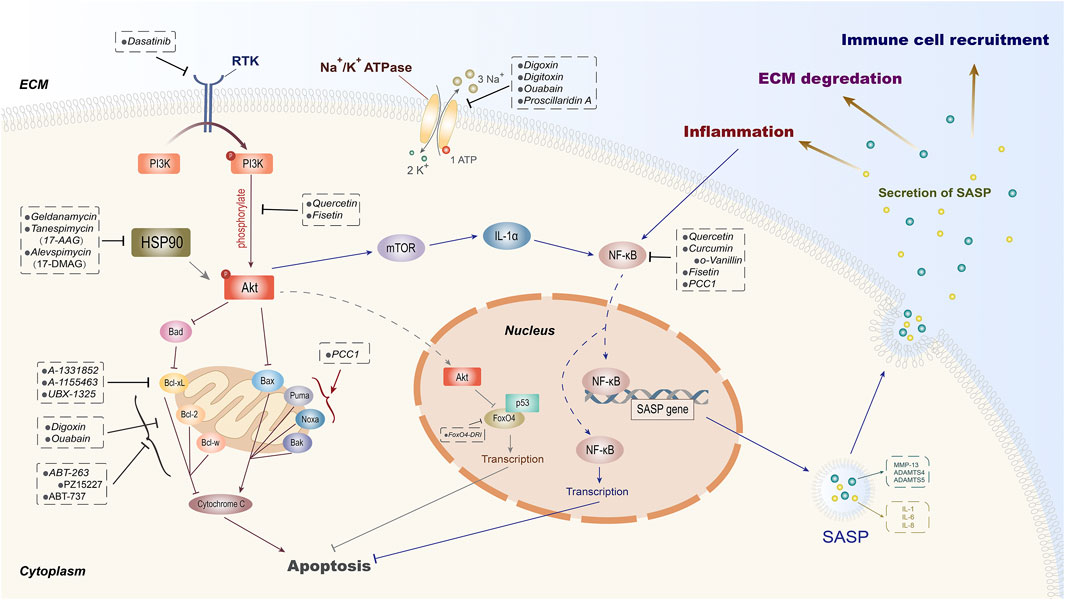
Frontiers | Senolytics: Eliminating Senescent Cells and Alleviating Intervertebral Disc Degeneration

Advancements in therapeutic drugs targeting of senescence - Mingsheng Zhu, Ping Meng, Xian Ling, Lili Zhou, 2020

Prospective Selective Mechanism of Emerging Senolytic Agents Derived from Flavonoids | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry